Edit QC Test Definitions
After adding a QC solution, the QC definitions can be edited to suit specific needs.
- About equation editing - provides basic general information on editing equations
- Equation editing - provides information on how to edit the equations
- Keyword summary - describes the keywords and operators available for use in equations
Define your own report values and pass requirements for any of the defined tests. The edited test definitions are saved with the worksheet, leaving the original tests intact.
To edit the QC test definition:
 |
You can add more than one of the same test. ICP Expert will increment the test name. |
- Rename the QC test in the QC Name field (optional).
- Click in the Report value field and edit the equation.
- Click in the Pass test field and edit the equation.
- Edit the pass/fail criteria in the Limits table.
 |
Right-click in the Report value and Pass test equation fields for a list of available names and mathematical operators. A red exclamation mark ! appears to the left of the equation field if the edited equation is not viable. |
 |
The ICP Expert software will automatically re-calculate the QC test results if any of the following are changed in the Limits table:
|
What are the default QC test definitions?
About Equation Editing
Right-click in either equation field to display a context menu listing the available keywords and operators that can be used in the field.
 |
The failure flag cannot be edited. |
The Limits table applies to the currently selected QC solution and can be edited in 2 ways:
- Select/deselect the checkbox to the left of the analyte wavelength label to select whether to apply the QC test to the wavelength or not. Checkbox indicated by the red oval in the image below.
- Entering appropriate values into columns visible to the right of the analyte wavelength label (depending on the QC test and equations used, the number and types of visible columns will change). If a limit column is referred to in the QC equations then the appropriate data must be entered in the table or the equation may evaluate to an error. If an evaluation error occurs during a worksheet analysis an 'S' flag will be raised in the worksheet Analysis page.
The Detection Limit table can be populated with appropriate MDL and CRQL data if required, and these values can be used in any QC test. If either of these columns is referred to in a QC test then appropriate values must be entered or the QC equation may report an error. If an evaluation error occurs during a worksheet analysis an 'S' flag will be raised in the worksheet Analysis page. See image below.
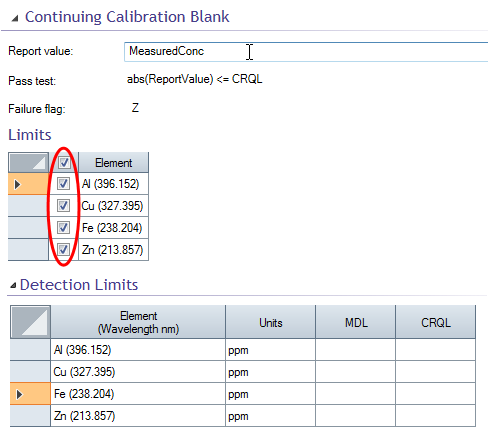
CCB test showing editing in the Report value and Detection Limits table.
Equation Editing
The report value and pass test equations can both be edited.
The equations are evaluated according to 'BODMAS' priority rules:
|
B |
Evaluate values/operations in enclosing brackets, for example, 2*(1+2)=6; |
|
O |
Evaluate orders (also known as exponents, powers), for example, 2*22=8; |
|
DM |
Evaluate division and multiplication (equal priority), with evaluation in order from left to right, for example, 2*3/2=3; |
|
AS |
Evaluate addition and subtraction (equal priority), with evaluation from left to right, for example, 1-2+3=2; |
|
|
Evaluate from left to right |
 |
The following comparison: a < b < c, where value b is evaluated against limits a and c; will result in a syntax error if comparisons are constructed this way in the equation fields. To achieve the same result the following syntax should be used: a < b and b < c. |
When logical operators are used in the pass test equation, evaluation always occurs left to right. Operands (functions and values to the left and right of the logical operator) are evaluated as per the BODMAS rules above before evaluating the logic test, for example, (1+2)*3 > 1/2*3 will simplify to 9 > 1.5 and evaluate to True.
Report Value
The report value equation can be edited to calculate appropriate values to be used in the Pass Test equation. The equation will be evaluated for each 'checked' element wavelength in the Limit Table.
The equation must evaluate to a numeric value, with all math operators and functions (+, -, *, /, abs) and numbers allowed. Logical operators (and, or, not, >, <, >=, =<, <>) cannot be used.
A number of keywords can also be used to refer to values in the Limits Table, Detection Limits Table, Measured Sample Concentration, Measured Sample Concentration RSD or Measured Sample Intensity RSD. Refer to Keyword Summary for details.
A red exclamation mark will be displayed to the left of the equation field if the equation evaluates to an error. Hover over the exclamation mark for hint text about the evaluation error. If an evaluation error occurs during a worksheet analysis an 'S' flag will be raised in the worksheet Analysis page.
If the equation is edited a 'reverse arrow' will be displayed to the right of the equation field. Clicking on this arrow will restore the equation to its 'default' value.
Pass Test
The pass test equation can be edited to evaluate the QC solution results against specific criteria. The equation will be evaluated for each 'checked' element wavelength in the Limit Table.
The equation must evaluate to a True or False value, all math operators and functions (+, -, *, /, abs) and logical operators (and, or, not, >, <, >=, =<, <>) are allowed.
A number of keywords can also be used to refer to values in the Limits Table, Detection Limits Table, Measured Sample Concentration, Measured Sample Concentration RSD or Measured Sample Intensity RSD. Refer to Keyword Summary for details.
A red exclamation mark will be displayed to the left of the equation field if the equation evaluates to an error. Hover over the exclamation mark for hint text about the evaluation error. If an evaluation error occurs during a worksheet analysis an 'S' flag will be raised in the worksheet Analysis page.
If the equation is edited a 'reverse arrow' will be displayed to the right of the equation field. Clicking on this arrow will restore the equation to its 'default' value.
Limits Table
Depending on the selected QC solution and the types of equations defined for the solution, different columns will be displayed.
For Blank tests, which may only refer to MDL or CRQL limits, only the checkbox column and element wavelength label will be visible.
Different QC solution types may also show any combination of Defined Concentration, Lower Limit, Upper Limit or Difference columns.
If any of the Limit Table fields (Defined Concentration, Lower Limit, Upper Limit or Difference) are referred to in a QC equation for the selected QC solution, then that column will become visible in the Limits Table for that solution.
Keyword Summary
Keywords used in QC equations can be loosely grouped into the following categories:
Variables
The use of these keywords will return the measured worksheet data for the current QC solution. When used with enclosing brackets and a reference to another solution (see below) they will return the measured worksheet data for the referenced solution.
|
Variable |
Description |
|
IntRSD |
Returns the %RSD of replicate intensity measurements. RSD is not returned as a percentage, for example, 5%RSD will return a value of 5 (not 0.05). |
|
ConcRSD |
Returns the %RSD of replicate concentration measurements. RSD is not returned as a percentage, for example, 5%RSD will return a value of 5 (not 0.05). |
|
MeasuredConc |
Returns the measured concentration (in the displayed units) after weight, volume and dilution factor corrections have been applied, in other words, it returns the concentration as displayed on the Analysis page. |
Solution References
These keywords must be used in conjunction with one of the variable keywords above, for example, MeasuredConc(PreviousSample), IntRSD(CCV), ConcRSD(DUP). The solution references available will be dependent on the QC solutions available in the worksheet. References to specific QC solution types will refer to the previous solution of that type in the sequence (previous to the selected QC solution).
|
Solution Reference |
Description |
|
CCB |
Returns a reference to the previous Continuing Calibration Blank solution |
|
CCV |
Returns a reference to the previous Continuing Calibration Verification solution |
|
CRS |
Returns a reference to the previous CRQL/CRDL Solution for ICP |
|
DUP |
Returns a reference to the previous Duplicate solution |
|
ICB |
Returns a reference to the previous Initial Calibration Blank solution |
|
ICSA |
Returns a reference to the previous ICSA solution |
|
ICV |
Returns a reference to the previous Initial Calibration Verification |
|
LCS |
Returns a reference to the previous Laboratory Control Sample |
|
MSD |
Returns a reference to the previous Matrix Spike Duplicate solution |
|
MSPK |
Returns a reference to the previous Matrix Spike solution |
|
PBLK |
Returns a reference to the previous Preparation Blank solution |
|
QCSPK |
Returns a reference to the previous QC Spike solution |
|
SER |
Returns a reference to the previous Serial Dilution solution |
|
PreviousSolution |
Returns a reference to the previous solution (including QC/Calibration solutions) |
|
PreviousSample |
Returns a reference to the previous sample solution (excludes QC/Calibration solutions) |
Constants
These keywords return the values from the Report Value equation, data entered in the Limits Table or data entered in the Detection Limit table.
|
Constant |
Description |
|
MDL |
Returns the value entered in the MDL table |
|
CRQL |
Returns the value entered in the CRQL table |
|
DefinedConc |
Returns the value in the Defined Concentration column of the Limits Table |
|
LowerLimit |
Returns the value in the Lower Limit column of the Limits Table |
|
UpperLimit |
Returns the value in the Upper Limit column of the Limits Table |
|
PercentDiff |
Returns the value in the Difference column of the Limits Table |
|
ReportValue |
Returns the value calculated from the Report Value equation |
Operators and Functions
These keywords are used to perform mathematical and logical comparison operations.
|
Operator |
Name |
Description |
|
+ |
Plus (add) |
Math Operator, adds 2 numbers |
|
- |
Minus (subtract) |
Math Operator, subtracts 1 number from another |
|
* |
Multiply (product) |
Math Operator, multiplies one number by another |
|
= |
Equal to |
Logical Operator, compares equality of 2 terms, for example, 1=1 is True |
|
/ |
Divide |
Math Operator, divides one number by another |
|
() |
Enclosing Brackets |
Math/Logical Operator, encloses math or logical operations such that they are evaluated before other operations |
|
abs |
Absolute Value (positive value) |
Math Function, returns the positive value of a number or function |
|
<> |
Not Equal To |
Logical Operator, compares inequality of 2 terms, for example, 1<>1 is False |
|
> |
Greater Than |
Logical Operator, compares magnitude of 2 terms, for example, 1>2 is False |
|
< |
Less Than |
Logical Operator, compares magnitude of 2 terms, for example, 1<2 is True |
|
>= |
Greater Than or Equal To |
Logical Operator, compares equality and magnitude of 2 terms, for example, 1>=1 is True |
|
<= |
Less Than or Equal To |
Logical Operator, compares equality and magnitude of 2 terms, for example, 2<=1 is False |
|
not |
Not |
Logical Operator, negates the following term, for example, not True is False |
|
and |
And |
Logical Operator, combines 2 logical comparisons, both of which must be True to evaluate to True, for example, 1>2 and 1<2 will evaluate to False |
|
or |
Or |
Logical Operator, combines 2 logical comparisons, either of which can be True to evaluate to True, for example, 1>2 or 1<2 will evaluate to True |
See also: